
Am Fam Physician. 2025;112(6):683-684
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
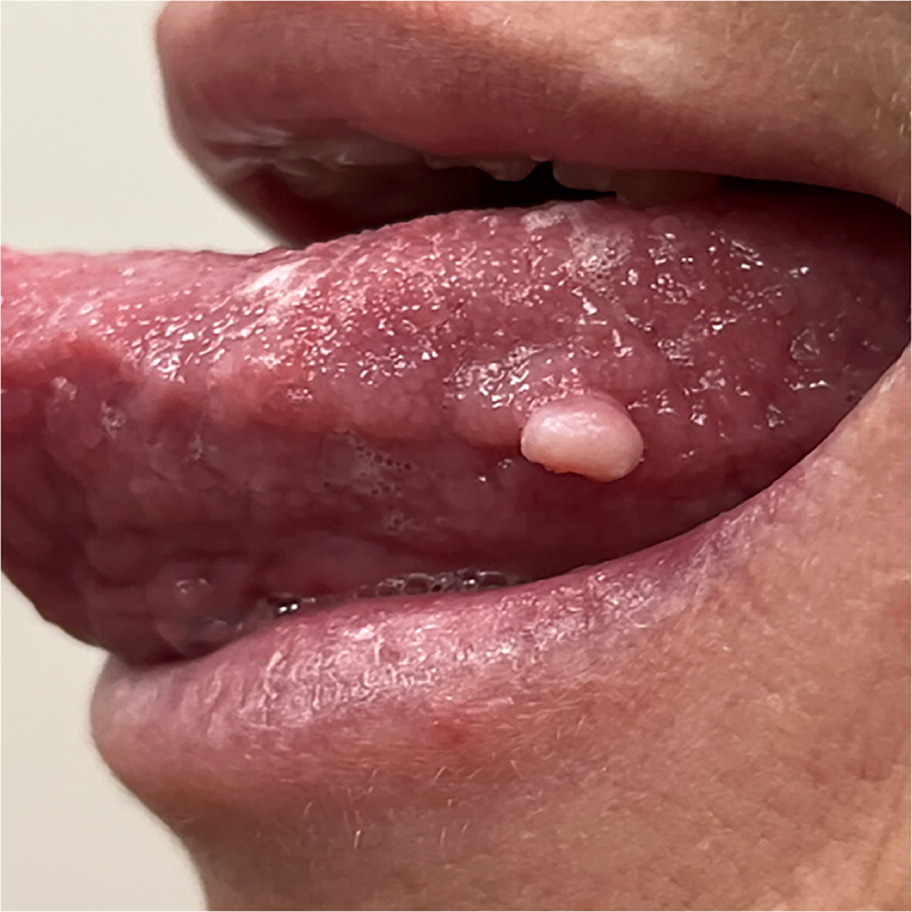
A 47-year-old woman presented with a solitary raised lesion on her tongue that developed 1 week earlier. Initially, the lesion was red, but it changed to white-pink. It was not painful and did not interfere with chewing, but it occasionally affected her speech. She had no history of trauma, including tongue biting, and no other oral lesions. The patient had no increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sour stimuli, and she reported no loss or change in taste or other associated symptoms.
Physical examination revealed a 2- × 3-mm, white-pink papule on the left lateral tongue (Figure 1). It was not tender and did not express pus or fluid. No lymph node swelling was detected.
QUESTION
Based on the patient's history and physical examination, which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Giant cell fibroma.
B. Lymphoepithelial cyst.
C. Mucocele.
D. Squamous papilloma.
DISCUSSION
The answer is D: squamous papilloma, which usually occurs as a single, pedunculated or sessile growth of squamous epithelium with papillary projections.1 The surface can appear rounded or cauliflower-like or resemble a finger.2 Squamous papillomas are usually less than 1 cm in size.2 They commonly appear white or red-pink, but the color depends on the level of keratinization, with highly keratinized lesions appearing white.1,2
Subscribe
From $180- Immediate, unlimited access to all AFP content
- More than 125 CME credits/year
- AAFP app access
- Print delivery available
Issue Access
$59.95- Immediate, unlimited access to this issue's content
- CME credits
- AAFP app access
- Print delivery available
