
Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(8):1327-1328
See related article on Hirschsprung's disease.
What is Hirschsprung’s Disease?
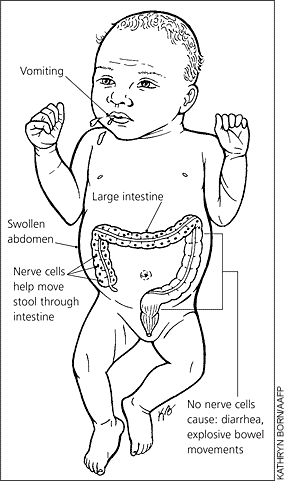
People with Hirschsprung’s (HERSH-sprungz) disease don’t have certain nerve cells in their large bowel (part of the digestive system). These cells are called ganglion (gang-GLEE-on) cells. The bowel won’t work right without them (see drawing). Most people with this disease start having problems when they are babies.
What are the symptoms?
Babies with this disease usually have trouble passing stools and don’t eat like other babies. They may have diarrhea or constipation, and their stomach may be swollen. They may not grow or gain weight like other babies.
How can my doctor tell if my baby has the disease?
Your doctor may give your child special tests or send you to a specialist. The specialist may test a small piece of your baby’s intestines to tell if your baby has the disease.
How is it treated?
Most children with the disease need surgery. The surgeon will take out the part of the bowel that doesn’t have ganglion cells.
Most children with the disease live normal lives after they heal from surgery. Some have problems passing stools. Eating foods that are high in fiber (for example, certain fruits and vegetables and whole grains) can help.
Some children get an infection in their bowel after surgery. The infection usually causes bad-smelling, watery stools. You should watch for this infection for up to 10 years after your child’s surgery. If you think your child has an infection, take him or her to the doctor right away.
Where can I get more information?
Your doctor
American Academy of Family Physicians
Web site: https://familydoctor.org
American Pediatric Surgical Association
Web site:http://www.eapsa.org/parents/hirschsprungs.cfm
Telephone: 1–847–480–9576
Hirschsprung’s and Motility Disorders Support Network
Web site:http://www.hirschsprungs.info
International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
Web site:http://www.aboutkidsgi.org/hirschsprungs.html
Telephone: 1–888–964–2001
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Web site:http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/hirschsprungs_ez/
Telephone: 1–800–891–5389
United Ostomy Associations of America
Web site:http://www.uoaa.org
Telephone: 1–800–826–0826