Editor's Note: This article has been updated to incorporate the February 2023 guidance update from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
This is a corrected version of the article that appeared in print.
Am Fam Physician. 2022;106(3):270-278
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Each year, malaria causes an estimated 500,000 deaths worldwide. Most of these deaths occur in Africa and disproportionally affect children younger than five years worldwide. Human malarial disease is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium. The primary means of infection is through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito. The incidence of malaria in the United States has increased since 2011, in conjunction with the increase in worldwide travel. An estimated 2,000 cases of malaria occur annually in the United States. All travelers to malaria-endemic regions should be prescribed prophylaxis. Malaria has a broad range of clinical presentations. Travelers who have symptoms of malaria should seek medical attention as soon as possible. All febrile travelers who have recently returned from a malarious area should be evaluated for malaria. The accurate, timely, and species-specific diagnosis of malaria is essential for successful treatment. Direct microscopy of Giemsa-stained blood smears is the reference standard for laboratory diagnosis. Rapid testing for malaria has emerged as an important adjunctive diagnostic modality. Malaria treatment is determined by individual patient factors and geography. The World Health Organization recommends treating uncomplicated cases of malaria with artemisinin combination therapy. [corrected] Severe malaria is mainly caused by Plasmodium falciparum. Children, pregnant patients, and people who are not from endemic regions are at highest risk of severe malaria. Intravenous artesunate is the treatment of choice for severe malaria.
Malaria has infected humans since the beginning of recorded history.1 Some estimates place its total mortality burden at one-half of all people who have ever lived.2 Each year, the disease continues to cause an estimated 500,000 deaths worldwide.2 Most of these deaths occur in Africa and disproportionally affect children younger than five years worldwide.3
| The incidence of malaria in the United States has increased since 2011, in conjunction with the increase in worldwide travel. An estimated 2,000 cases of malaria occur annually in the United States. |
| Rapid testing is an adjunctive diagnostic modality for malaria with excellent sensitivity and negative predictive value. In the United States, malaria rapid diagnostic tests should be used only in conjunction with thick and thin blood smears. |
| The first malaria vaccine approved for widespread use was recently recommended by the World Health Organization for the prevention of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children living in endemic areas. |
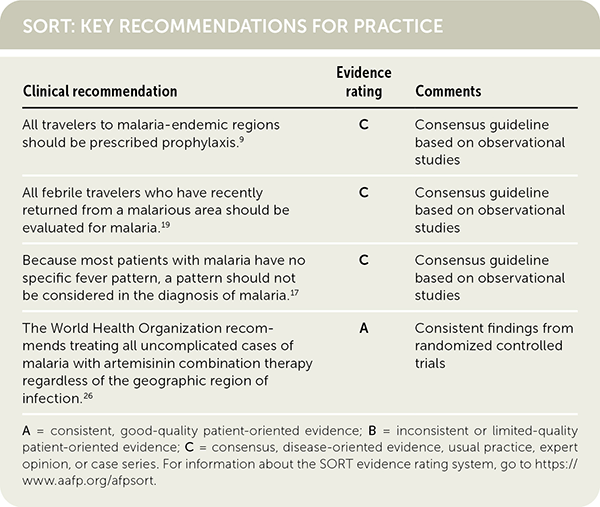
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| All travelers to malaria-endemic regions should be prescribed prophylaxis.9 | C | Consensus guideline based on observational studies |
| All febrile travelers who have recently returned from a malarious area should be evaluated for malaria.19 | C | Consensus guideline based on observational studies |
| Because most patients with malaria have no specific fever pattern, a pattern should not be considered in the diagnosis of malaria.17 | C | Consensus guideline based on observational studies |
| The World Health Organization recommends treating all uncomplicated cases of malaria with artemisinin combination therapy, regardless of the geographic region of infection.26 [corrected] | A | Consistent findings from randomized controlled trials |
Human malarial disease is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which has five known species: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and the emerging zoonotic parasite P. knowlesi. Most deaths are caused by P. falciparum.4 The primary means of human infection is through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito.
Malaria poses a threat to one-half of the world's population.5 The incidence of malaria in the United States has continued to increase annually since 2011, in conjunction with the increase in worldwide travel.6 Malaria, formerly endemic to the United States, was successfully eradicated in the country during the mid-20th century.7 In the United States today, malaria is almost exclusively found in travelers to and immigrants from endemic regions of the world.7 However, transmission can rarely occur via other means, such as exposure to infected blood products, congenital transmission, or local mosquito-borne outbreaks.8 In the United States, an estimated 2,000 cases of malaria occur annually.7
Prevention
Before a patient travels internationally, the physician should conduct a personalized risk assessment, including travel location, the season of travel, and the proposed itinerary. The regions with the highest rates of malaria transmission are sub-Saharan Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and Southeast Asia. The risk of contracting malaria varies seasonally, with the highest risk occurring during and just after the rainy season, typically between May and December.9
The primary method of malaria prevention is avoiding mosquito bites. Anopheles mosquitoes primarily feed at night; most malaria transmission occurs between dusk and dawn. Prevention strategies include personal protective measures such as using insecticide-treated bed nets, wearing clothes that minimize exposed skin, and applying mosquito-repelling chemicals. The most effective insect repellents contain 20% to 30% N, N-diethyl- m-toluamide (DEET) or 20% picaridin.10 Higher concentrations are not associated with greater protection. Applying permethrin to clothing increases protection against penetrating insect bites.11
All travelers to malaria-endemic regions should be prescribed prophylaxis.9 The choice of agent should be based on location and duration of travel, malarial resistance patterns, and the patient's medical history (Table 112,13). All prevention regimens involve beginning the medication before departure, taking the medication while in the high-risk area, and continuing the medication for a defined period after travel has ended. The use of antimalarial agents does not negate the need for personal protective measures. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides country-specific prophylaxis recommendations at http://www.cdc.gov/malaria/travelers/country_table/a.html.

| Drug* | Timing | Adult dosing and cost† | Child dosing | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroquine-sensitive malaria | ||||
| Chloroquine | Begin one to two weeks before travel and continue for four weeks after leaving malaria-endemic area | 500 mg salt (300 mg base) once per week $50 (—) for six weeks | 8.3 mg salt (5 mg base) per kg once per week, up to adult dosage | Used for prophylaxis in Mexico and Central America (west of the Panama Canal) and the island of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic) In the United States, hydroxychloroquine may be better tolerated |
| Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) | Begin one to two weeks before travel and continue for four weeks after leaving malaria-endemic area | 400 mg salt (310 mg base) once per week $25 ($180) for eight weeks | 6.5 mg salt (5 mg base) per kg once per week, up to adult dosage | Chloroquine may exacerbate psoriasis May be used in all trimesters of pregnancy |
| Chloroquine-resistant malaria | ||||
| Atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone) | Begin one to two days before travel and continue for one week after leaving malaria-endemic area | 250 mg/100 mg once per day $55 ($220) for four weeks | Daily dose (one children's tablet is 62.5 mg/25 mg): < 5 kg: not recommended 5 kg to 8 kg: one-half of children's tablet 9 kg to 10 kg: three-fourths of children's tablet 11 kg to 20 kg: one children's tablet 21 kg to 30 kg: two children's tablets 31 kg to 40 kg: three children's tablets ≥ 40 kg: one adult tablet | Useful in regions of mefloquine resistance Do not use in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 [0.50 mL per second per m2]) Do not use in patients who are pregnant or in breastfeeding infants weighing < 5 kg Should be taken with food or a milky drink High cost makes this drug less practical for longer trips |
| Doxycycline | Begin one to two days before travel and continue for four weeks after leaving malaria-endemic area | 100 mg once per day $20 (varies by brand) for four weeks | 2.2 mg per kg per day, up to the adult dosage | Useful in regions of mefloquine resistance Do not use in children younger than eight years or in patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding May cause nausea, photosensitivity, vaginal yeast infections, and esophageal ulceration |
| Mefloquine | Begin two weeks or more before travel and continue for four weeks after leaving malaria-endemic area | 250 mg salt (228 mg base) once per week $25 (—) for six weeks | Weekly dose: ≤ 9 kg: 5 mg salt (4.6 mg base) per kg > 9 kg to 19 kg: one-fourth of 250-mg tablet 20 kg to 30 kg: one-half of 250-mg tablet 31 kg to 45 kg: three-fourths of 250-mg tablet ≥ 45 kg: one 250-mg tablet | Contraindications include epilepsy, psychiatric conditions (e.g., anxiety, depression), and cardiac conduction disorders May be used in all trimesters of pregnancy |
| Short-term travel to areas with more than 90% Plasmodium vivax malaria (e.g., Central and South America) | ||||
| Primaquine | Begin one to two days before travel and continue for one week after leaving malaria-endemic area | 52.6 mg salt (30 mg base) once per day $60 (—) for four weeks | 0.8 mg salt (0.5 mg base) per kg once per day, up to adult dosage | Screen for G6PD deficiency before use; can be fatal if taken by patients who are G6PD deficient Do not use in pregnant patients or in patients who are breastfeeding unless the infant has a documented normal G6PD level Less commonly used than other prophylactic drugs |
| Tafenoquine | See adult dosage | Loading dose: 200 mg once per day for three days before travel Maintenance dose: 200 mg once per week starting seven days after last loading dose Terminal dose: one 200-mg dose seven days after last maintenance dose (—) $280 per dose package (16 tablets) | Not recommended | Screen for G6PD deficiency before use Do not use in those with G6PD deficiency, children, and patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding Not recommended in those with an underlying psychotic disorder |
Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of malaria ranges from asymptomatic parasitemia or uncomplicated disease to severe disease or death. The differential diagnosis of malaria is summarized in Table 2.16 Symptoms of malaria can develop within six to seven days of exposure, but the presentation may be delayed for several months after leaving an endemic region.17 Symptomatic malaria is characterized by fevers, chills, headaches, myalgias, and malaise. It may also present as fever without a specific or obvious cause or as gastrointestinal symptoms in children. There are no typical features of malaria.10,17
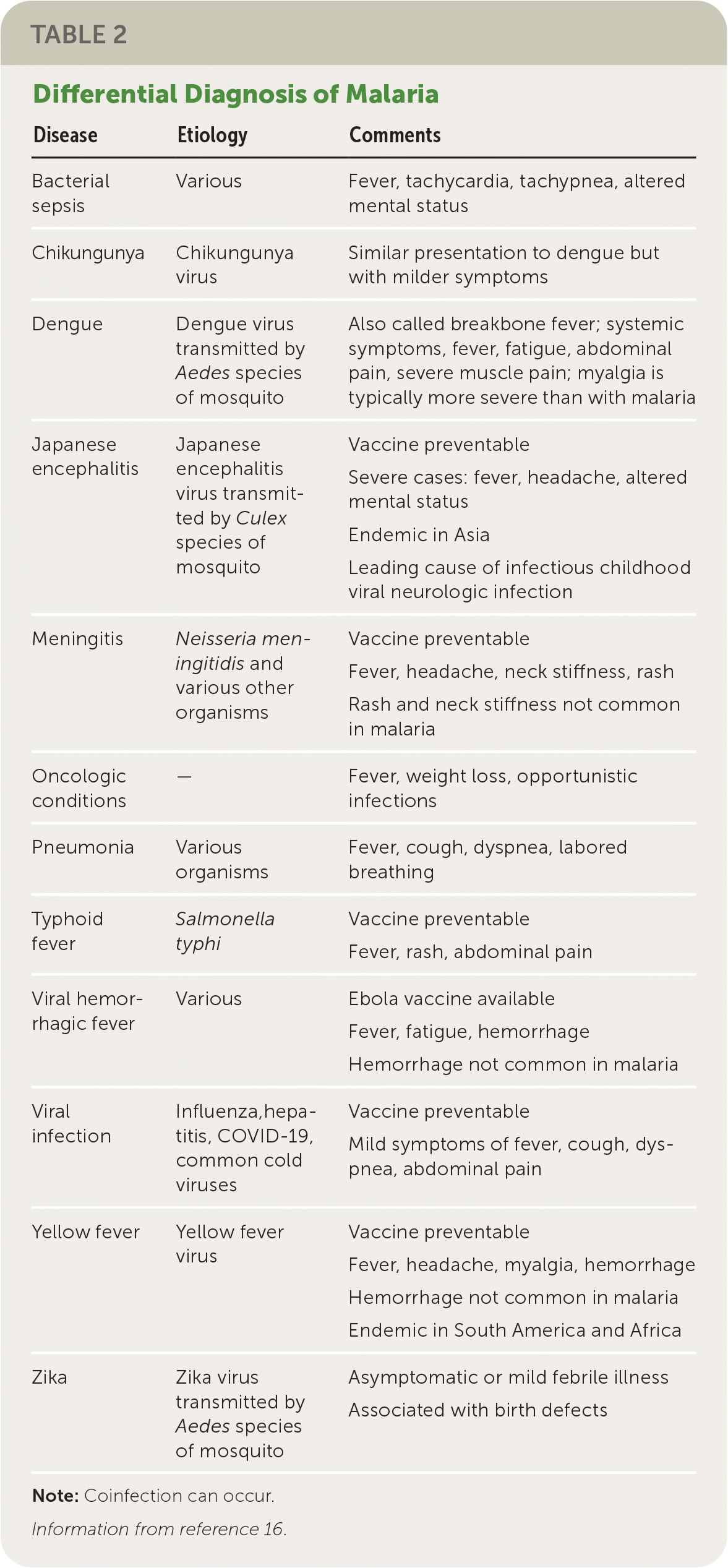
| Disease | Etiology | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial sepsis | Various | Fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, altered mental status |
| Chikungunya | Chikungunya virus | Similar presentation to dengue but with milder symptoms |
| Dengue | Dengue virus transmitted by Aedes species of mosquito | Also called breakbone fever; systemic symptoms, fever, fatigue, abdominal pain, severe muscle pain; myalgia is typically more severe than with malaria |
| Japanese encephalitis | Japanese encephalitis virus transmitted by Culex species of mosquito | Vaccine preventable Severe cases: fever, headache, altered mental status Endemic in Asia Leading cause of infectious childhood viral neurologic infection |
| Meningitis | Neisseria meningitidis and various other organisms | Vaccine preventable Fever, headache, neck stiffness, rash Rash and neck stiffness not common in malaria |
| Oncologic conditions | — | Fever, weight loss, opportunistic infections |
| Pneumonia | Various organisms | Fever, cough, dyspnea, labored breathing |
| Typhoid fever | Salmonella typhi | Vaccine preventable Fever, rash, abdominal pain |
| Viral hemorrhagic fever | Various | Ebola vaccine available Fever, fatigue, hemorrhage Hemorrhage not common in malaria |
| Viral infection | Influenza, hepatitis, COVID-19, common cold viruses | Vaccine preventable Mild symptoms of fever, cough, dyspnea, abdominal pain |
| Yellow fever | Yellow fever virus | Vaccine preventable Fever, headache, myalgia, hemorrhage Hemorrhage not common in malaria Endemic in South America and Africa |
| Zika | Zika virus transmitted by Aedes species of mosquito | Asymptomatic or mild febrile illness Associated with birth defects |
In the absence of a detailed travel history, malaria is often misdiagnosed as a nonspecific viral illness.18 Travelers who have symptoms of malaria should seek medical attention as soon as possible, regardless of whether prophylaxis or preventive measures were used. All febrile travelers who have recently returned from a malarious area should be evaluated for malaria.19 Suspicion of P. falciparum malaria is a medical emergency. Physicians should use only laboratory-based diagnostic methods.18 Because most patients with malaria have no specific fever pattern, a pattern should not be considered in the diagnosis.17 Clinical deterioration or death can occur within 24 to 36 hours in a malaria-naive patient.7
Diagnostic Testing
The accurate, timely, and species-specific diagnosis of malaria is essential for successful treatment. Microscopic examination of Giemsa-stained blood smears is the reference standard for laboratory diagnosis. Thick blood smears are used to detect the presence of malarial parasites, and thin blood smears are used to determine the species and quantify parasitemia.18,20 When malaria is suspected, urgent microscopy should be performed by an individual with expertise in examining blood smears and diagnosing malaria.17 Multiple blood smears may be needed to produce a positive result. Three negative results, 12 hours apart, are needed to rule out malaria.21
Rapid testing for malaria has emerged as an important adjunctive diagnostic modality. Rapid diagnostic tests have excellent sensitivity and negative predictive value with results available in five to 20 minutes.22,23 Rapid diagnostic tests for malaria are simple to use, do not require laboratory facilities or diagnostic expertise, and enable prompt diagnosis.24 However, rapid diagnostic tests can detect only P. falciparum and P. vivax, and they do not provide data regarding parasite density.17,23,24 In the United States, rapid diagnostic tests for malaria should be used only in conjunction with thick and thin blood smears.23,24 The usefulness of these rapid tests ends with diagnosis because further testing and monitoring must be completed via microscopy.23 Binax-NOW is the only rapid diagnostic test approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for malaria,25 but a variety of other assays are available worldwide.
Treatment
The CDC-recommended treatment of malaria is based on four variables: the clinical status of the patient (uncomplicated vs. severe disease), the species involved, the patient's history of prophylaxis, and the geographic region where the infection occurred.25 Under certain circumstances, laboratory testing may not be readily available. If clinical suspicion for malaria is high, empiric treatment should be initiated promptly, especially in the setting of severe disease. Patients who used prophylaxis should be treated with different antimalarial medications than those used for prophylaxis.13,25,26
Patients who are immunocompromised, patients with no previous malarial immunity, children, pregnant patients, and patients with signs of severe disease should be hospitalized. Severe disease is defined as the presence of at least one of the following: impaired consciousness (Glasgow Coma Scale score less than 11), convulsions, severe anemia (hemoglobin less than 7 g per dL [70 g per L] in adults or less than 5 g per dL [50 g per L] in children younger than 12 years), acute kidney injury, hypoglycemia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, acidosis, coma, liver dysfunction, or parasite density greater than 5%.25
Hospitalized patients should receive standard supportive care, including intravenous fluids, antipyretics, and antiemetics. Outpatient treatment with close clinical follow-up can be considered in patients without an indication for hospitalization. Malaria specialists are available 24 hours a day, seven days a week to aid physicians with diagnosis and treatment (Table 3).

| 770-488-7788 |
| 855-856-4713 (toll free) |
| 770-488-7100 (outside of normal hours*) |
UNCOMPLICATED MALARIA
The World Health Organization recommends treating uncomplicated cases of malaria with artemisinin combination therapy (ACT), which comprises an artemisinin derivative and a partner drug. However, artemisinin should not be used in the first trimester of pregnancy with the exception of artemether/lumefantrine (Coartem), which is acceptable for all trimesters (https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/new_info/2023/Coartem.html).26 [corrected] ACTs are well tolerated and highly effective against all Plasmodium species. Patients should be informed that counterfeit and substandard antimalarials are widespread in resource-limited and lower-income countries.
Malaria Caused by Plasmodium falciparum or Unknown Species. If ACT is not available and the infection likely occurred in an area with chloroquine-sensitivity, chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) may be used. If ACT is unavailable and the infection occurred in an area with chloroquine resistance, atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone), a combination of quinine (Qualaquin) plus tetracycline, doxycycline, or clindamycin (Cleocin) should be used. Mefloquine is a treatment of last resort. Table 4 summarizes treatment options for acute uncomplicated malaria.25,26

| Drug* | Adult dosing and cost† | Child dosing | Special considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artemether/lumefantrine (Coartem) | One tablet is 20 mg/120 mg; four tablets per dose Three-day course (24 total tablets): Day 1: initial dose followed by repeat dose eight hours later Days 2 and 3: one dose every 12 hours — ($130) for treatment course | One tablet is 20 mg/120 mg 5 kg to < 15 kg: one tablet per dose 15 kg to < 25 kg: two tablets per dose 25 kg to < 35 kg: three tablets per dose ≥ 35 kg: four tablets per dose Three-day course (number of tablets varies): same as adults | Take with high-fat foods for best absorption Crush and mix with 10 mL of water if unable to swallow tablets Repeat dose if vomiting occurs less than two hours after treatment |
| Atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone) | Four tablets once per day for three days (one adult tablet is 250 mg/100 mg) $25 ($90) for treatment course | One children's tablet is 62.5 mg/25 mg Daily dose taken for three days: 5 kg to < 8 kg: two children's tablets 8 kg to < 10 kg: three children's tablets 10 kg to < 20 kg: one adult tablet 20 kg to < 30 kg: two adult tablets 30 kg to < 40 kg: three adult tablets ≥ 40 kg: four adult tablets | Consider alternative treatment in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 [0.50 mL per second per m2]) Take with food for best absorption Repeat dose if vomiting occurs less than one hour after treatment (less than 30 minutes for children) Crush and mix with water or milk if unable to swallow tablet Use for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria acquired from countries with artemisinin resistance |
| Chloroquine | 1 g salt (600 mg base) on day 1, followed by 500 mg salt (300 mg base) six, 24, and 48 hours after initial dose (total of four doses) $55 (—) for treatment course | 16.7 mg salt (10 mg base) per kg on day 1, followed by 8.3 mg salt (5 mg base) per kg six, 24, and 48 hours after initial dose (total of four doses) | Only for treatment of nonsevere infections from regions with chloroquine sensitivity Do not use if chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine was used for prophylaxis |
| Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) | 800 mg salt (620 mg base) on day 1, followed by 400 mg salt (310 mg base) six, 24, and 48 hours after initial dose (total of four doses) $15 ($120) for treatment course | 12.9 mg salt (10 mg base) per kg (maximum 800 mg per dose) on day 1, followed by 6.5 mg salt (5 mg base) per kg six, 24, and 48 hours after initial dose (total of four doses) | May be used in all trimesters of pregnancy |
| Quinine (Qualaquin) plus doxycycline, tetracycline, or clindamycin (Cleocin) | Quinine: 648 mg salt (542 mg base) three times per day for three to seven days; $40 ($130) for three-day treatment course Doxycycline: 100 mg twice per day for seven days; $10 (varies by brand) for treatment course Tetracycline: 250 mg four times per day for seven days; $40 (—) for treatment course Clindamycin: 20 mg per kg per day in three divided doses for seven days; $10 ($10) for treatment course in a patient weighing 70 kg | Quinine: 10 mg salt (8.3 mg base) per kg three times per day for three to seven days Doxycycline: 2.2 mg per kg twice per day for seven days Tetracycline: 25 mg per kg per day in four divided doses for seven days Clindamycin: 20 mg per kg per day in three divided doses for seven days | Administer quinine for three days unless infection occurred in Southeast Asia, in which case administer for seven days Doxycycline and tetracycline are favored over clindamycin but are not recommended during pregnancy or for children younger than eight years |
| Mefloquine | 750 mg salt (684 mg base) on day 1, followed by 500 mg (456 mg base) six to 12 hours after initial dose (total of two doses) $15 (—) for treatment course | 15 mg salt (13.7 mg base) per kg on day 1, followed by 10 mg salt (9.1 mg base) per kg six to 12 hours after initial dose (total of two doses) Do not exceed 500 mg per dose | Use only if no other treatment options are available Not recommended for infections acquired in Southeast Asia Associated with neuropsychiatric effects May be used in all trimesters of pregnancy |
Malaria Caused by Plasmodium ovale or Plasmodium vivax. Initial treatment is the same as for uncomplicated malaria due to P. falciparum or unknown species, as described previously. In addition, patients infected with P. ovale or P. vivax require treatment against hypnozoites (dormant forms), which are responsible for relapsing infections. Patients should be tested for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency because the drugs of choice, primaquine and tafenoquine, are associated with hemolytic anemia in people with G6PD deficiency. Tafenoquine should not be used in patients younger than 16 years or in patients with neuropsychiatric disorders. Tafenoquine is used only if chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine was used for the acute infection.
For people with G6PD deficiency who cannot tolerate primaquine or tafenoquine, chloroquine prophylaxis should be continued for one year. In those with intermediate G6PD deficiency, primaquine may be considered in close consultation with infectious disease or tropical medicine specialists. Table 5 summarizes antirelapse treatment options.25,26
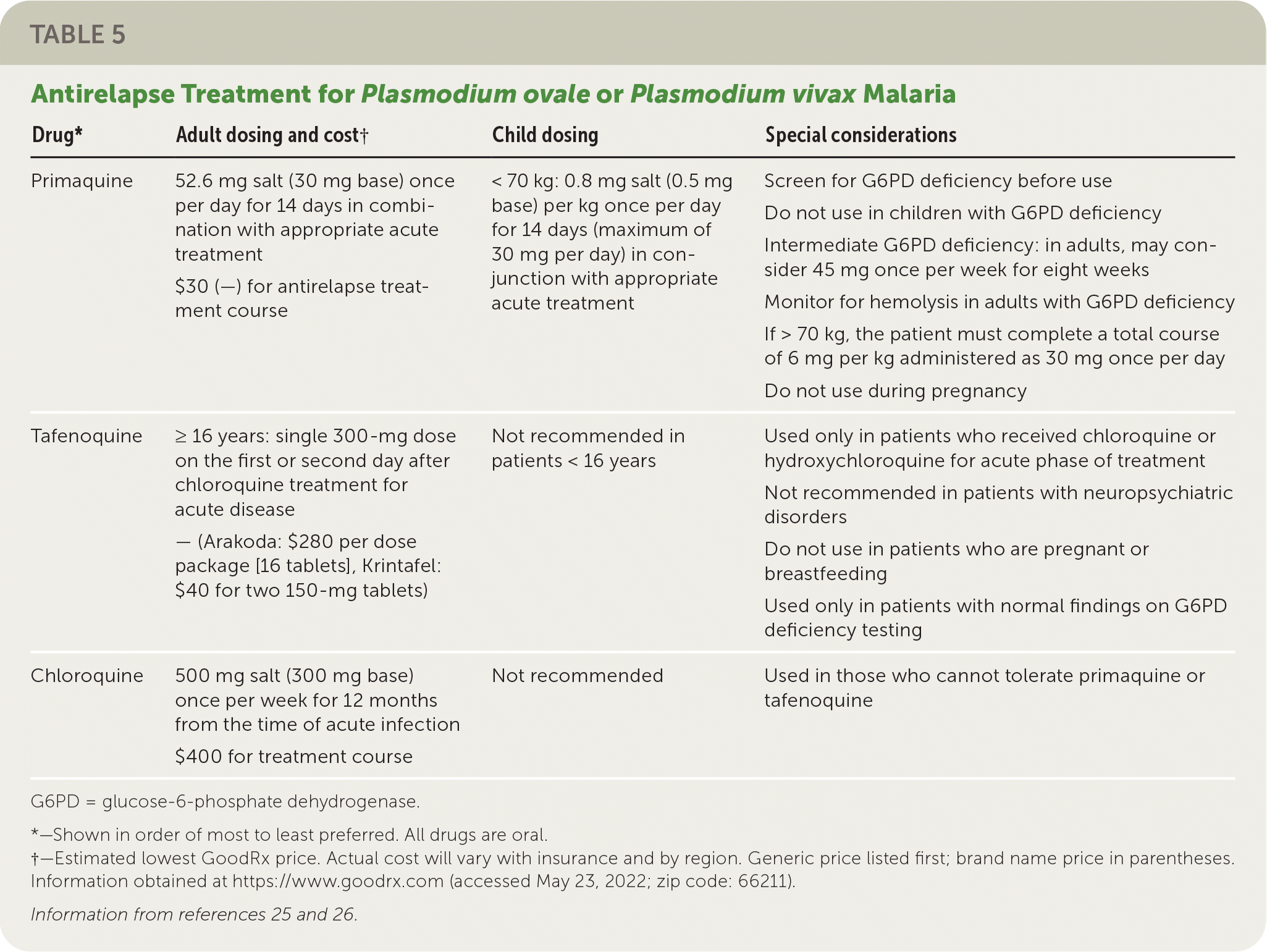
| Drug* | Adult dosing and cost† | Child dosing | Special considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primaquine | 52.6 mg salt (30 mg base) once per day for 14 days in combination with appropriate acute treatment $30 (—) for antirelapse treatment course | < 70 kg: 0.8 mg salt (0.5 mg base) per kg once per day for 14 days (maximum of 30 mg per day) in conjunction with appropriate acute treatment | Screen for G6PD deficiency before use Do not use in children with G6PD deficiency Intermediate G6PD deficiency: in adults, may consider 45 mg once per week for eight weeks Monitor for hemolysis in adults with G6PD deficiency If > 70 kg, the patient must complete a total course of 6 mg per kg administered as 30 mg once per day Do not use during pregnancy |
| Tafenoquine | ≥ 16 years: single 300-mg dose on the first or second day after chloroquine treatment for acute disease — (Arakoda: $280 per dose package [16 tablets], Krintafel: $40 for two 150-mg tablets) | Not recommended in patients < 16 years | Used only in patients who received chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine for acute phase of treatment Not recommended in patients with neuropsychiatric disorders Do not use in patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding Used only in patients with normal findings on G6PD deficiency testing |
| Chloroquine | 500 mg salt (300 mg base) once per week for 12 months from the time of acute infection $400 for treatment course | Not recommended | Used in those who cannot tolerate primaquine or tafenoquine |
Malaria Caused by Plasmodium malariae or Plasmodium knowlesi. Although resistance to chloroquines is not widely documented with P. malariae or P. knowlesi, the World Health Organization recommends the use of ACT, regardless of geographic region of infection.26 P. knowlesi is associated with severe disease, and patients should be hospitalized if this species is isolated. If ACT is not available and the infection is likely from a chloroquine-sensitive area, chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine may be used.25,26
SEVERE MALARIA
P. falciparum and, to a lesser degree, P. knowlesi cause almost all cases of severe malaria.26 Children, pregnant patients, and people who are not from endemic regions are at highest risk of severe malaria. Intravenous artesunate is the treatment of choice for severe disease and should be initiated as soon as possible (Table 6).25,26 The dosage for adults and children is 2.4 mg per kg at 0, 12, and 24 hours. Blood smears should be obtained every 12 hours. If the parasite density is less than 1% at least four hours after the third dose, the patient should be transitioned to a full course of an oral medication, ideally ACT. If the parasite density is greater than 1% after the third artesunate dose, artesunate should be continued as a single daily dose until parasitemia is less than 1%, not to exceed seven days. Artesunate is well tolerated, and allergy to artemisinins is the only absolute contraindication.25,26
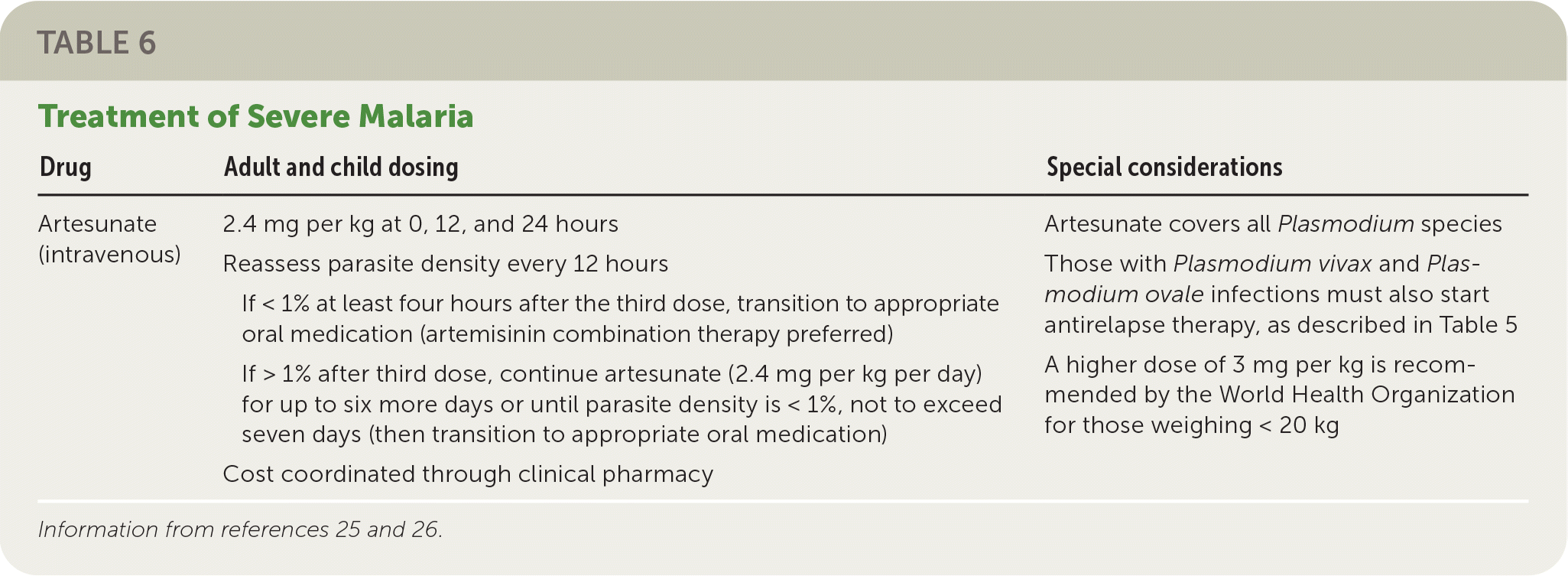
| Drug | Adult and child dosing | Special considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Artesunate (intravenous) | 2.4 mg per kg at 0, 12, and 24 hours Reassess parasite density every 12 hours If < 1% at least four hours after the third dose, transition to appropriate oral medication (artemisinin combination therapy preferred) If > 1% after third dose, continue artesunate (2.4 mg per kg per day) for up to six more days or until parasite density is < 1%, not to exceed seven days (then transition to appropriate oral medication) Cost coordinated through clinical pharmacy | Artesunate covers all Plasmodium species Those with Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale infections must also start antirelapse therapy, as described in Table 5 A higher dose of 3 mg per kg is recommended by the World Health Organization for those weighing < 20 kg |
If artesunate is not immediately available, the preferred oral medication for severe disease is artemether/lumefantrine (Coartem). Other options also include atovaquone/proguanil, quinine, and mefloquine. Tetracyclines and clindamycin should not be used because of their delayed onset of action. Once intravenous artesunate therapy becomes available, the oral medication should be discontinued.
The CDC no longer recommends the use of exchange transfusions as an adjunctive therapy for severe malaria.25 All patients treated for severe malaria should be evaluated for hemolytic anemia within 30 days after completing treatment.
PREGNANT PATIENTS
Malaria is associated with significant morbidity and mortality in pregnant patients. ACTs may be used in the second and third trimesters except for artemether/lumefantrine, which may be used in the first trimester as well. [corrected] Chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and quinine with clindamycin or mefloquine may be used throughout pregnancy. Artemether/lumefantrine may be used in the first trimester if no other options are available. Primaquine should not be used during pregnancy. Tafenoquine should not be used in patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Infants born to mothers who had P. vivax or P. ovale infection during pregnancy should be tested for G6PD deficiency. If results are normal, the mother should be treated with primaquine while breastfeeding. If G6PD deficiency is diagnosed, chloroquine should be used for one year after the initial treatment to prevent relapse.25,26
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Johnson and Kalra,8 Lo Re and Gluckman,27 and Juckett.28
Data Sources: PubMed was searched using the key words prevention, diagnosis, treatment, malaria, surveillance, travel medicine, chemoprophylaxis, and malaria treatment. The search was limited to English-language studies published since 2000. Secondary references from the key articles identified by the search were also used. Search dates: January 2018, October 2021, June 2022.
The opinions and assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of the U.S. Army Medical Department or the U.S. Army at large.