This is a corrected version of the article that appeared in print.
Am Fam Physician. 2024;109(2):119-129
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Foot fractures account for about one-third of lower extremity fractures in adults. They are typically caused by a crush injury or an axial or twisting force on the foot. Patients usually present with bony point tenderness and swelling of the affected area. Weight-bearing varies based on the extent of the fracture and the patient's pain tolerance. When a foot or toe fracture is suspected, anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique radiography with weight-bearing should be obtained. The Ottawa foot and ankle rules can help determine the need for radiography after an acute ankle inversion injury. Many foot fractures can be managed with a short leg cast or boot or a hard-soled shoe. Weight-bearing and duration of immobilization are based on the stability of the fracture and the patient's pain level. Most toe fractures can be managed nonsurgically with a hard-soled shoe for two to six weeks. Close attention should be paid to the great toe because of its role in weight-bearing, and physicians should follow specific guidelines for orthopedic referral. Meta-tarsal shaft fractures are managed with a boot or hard-soled shoe for three to six weeks. The proximal aspect of the fifth metatarsal has varied rates of healing due to poor blood supply, and management is based on the fracture zone. Lis-franc fractures are often overlooked; radiography with weight-bearing should be obtained, and physicians should look for widening of the tarsometatarsal joint. Other tarsal bone fractures can be managed with a short leg cast or boot for four to six weeks when nonsurgical treatment is indicated. Common foot fracture complications include arthritis, infection, malunion or nonunion, and compartment syndrome.
Foot fractures account for approximately one-third of lower extremity fractures in adults.1–3 Many foot fractures, especially in the forefoot, can be managed nonoperatively. Fractures in the foot may be masked by soft tissue injuries, and a high index of suspicion is required to avoid missing a fracture. This article discusses types of foot fractures, common mechanisms of injury, nonsurgical management, and indications for orthopedic referral. Table 1 summarizes the management of foot fractures.4–13 Foot fractures in children, ankle fractures, bony stress injuries, and guidance for athletes are beyond the scope of this manuscript.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Phalangeal fractures of the lesser toes with no rotation and less than 25% joint involvement can be managed nonsurgically.4,5,15 | C | Clinical reviews and consensus expert opinion |
| Metatarsal shaft fractures of the second through fourth metatarsals should be reduced when there is more than 3 to 4 mm of displacement or more than 10 degrees of angulation.4,5,21 | C | Clinical review and consensus expert opinion |
| Surgical management of a zone 2 or 3 proximal fifth metatarsal fracture should be considered in active patients to decrease the risk of nonunion.8,9,25 | B | Clinical reviews and one systematic review of patient-oriented outcomes |
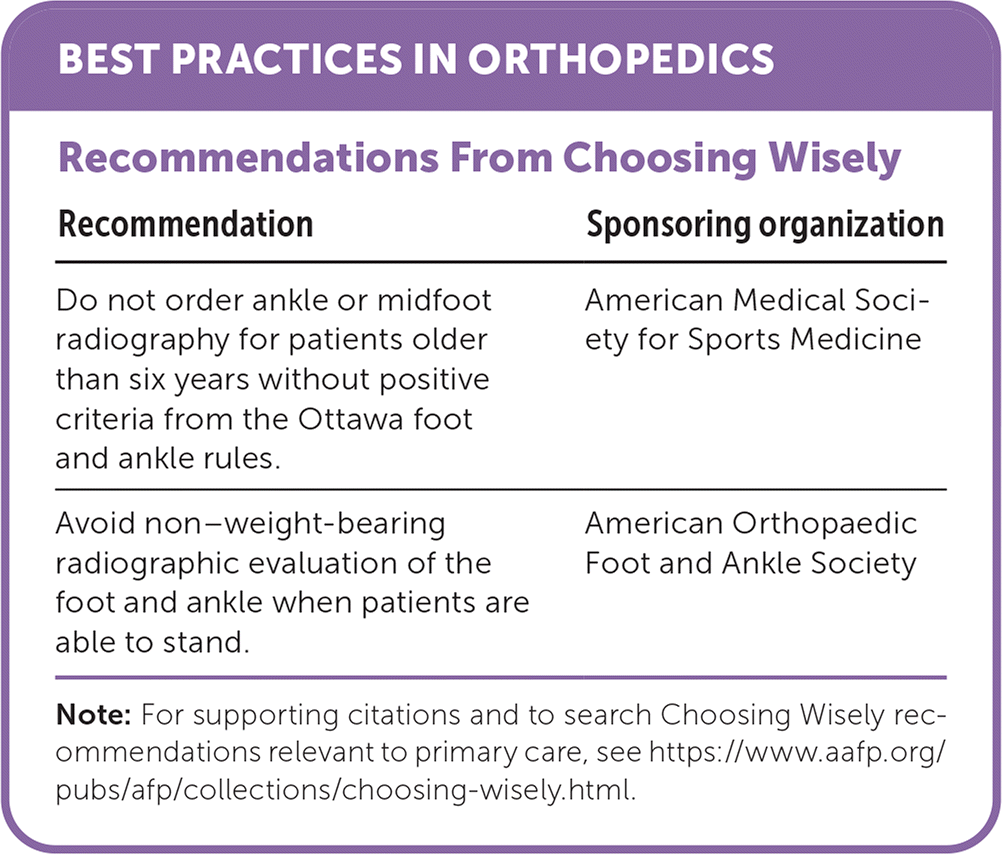
| Recommendation | Sponsoring organization |
|---|---|
| Do not order ankle or midfoot radiography for patients older than six years without positive criteria from the Ottawa foot and ankle rules. | American Medical Society for Sports Medicine |
| Avoid non–weight-bearing radiographic evaluation of the foot and ankle when patients are able to stand. | American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society |
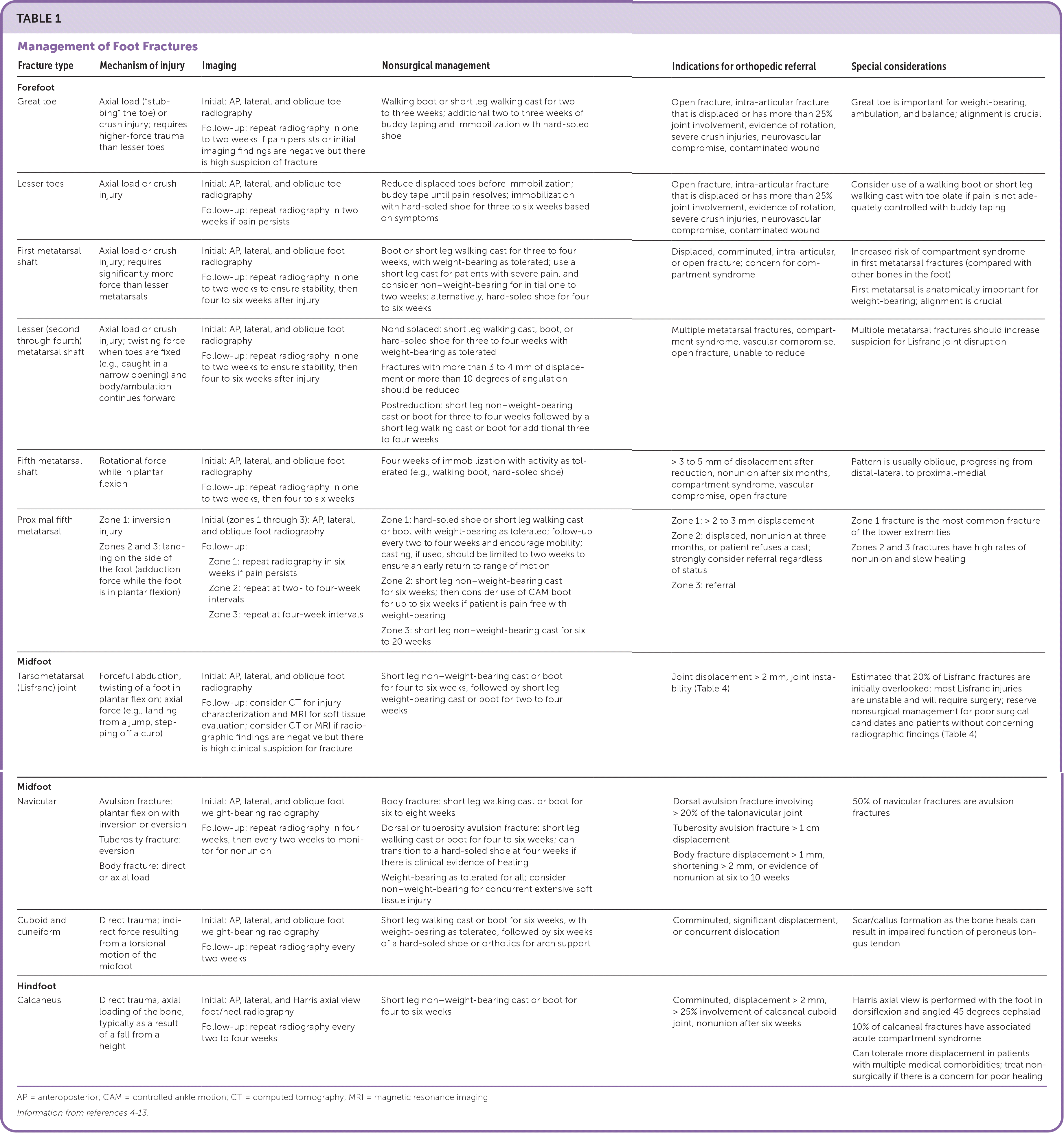
| Fracture type | Mechanism of injury | Imaging | Nonsurgical management | Indications for orthopedic referral | Special considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forefoot | |||||
| Great toe | Axial load (“stubbing” the toe) or crush injury; requires higher-force trauma than lesser toes | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique toe radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography in one to two weeks if pain persists or initial imaging findings are negative but there is high suspicion of fracture | Walking boot or short leg walking cast for two to three weeks; additional two to three weeks of buddy taping and immobilization with hard-soled shoe | Open fracture, intra-articular fracture that is displaced or has more than 25% joint involvement, evidence of rotation, severe crush injuries, neurovascular compromise, contaminated wound | Great toe is important for weight-bearing, ambulation, and balance; alignment is crucial |
| Lesser toes | Axial load or crush injury | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique toe radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography in two weeks if pain persists | Reduce displaced toes before immobilization; buddy tape until pain resolves; immobilization with hard-soled shoe for three to six weeks based on symptoms | Open fracture, intra-articular fracture that is displaced or has more than 25% joint involvement, evidence of rotation, severe crush injuries, neurovascular compromise, contaminated wound | Consider use of a walking boot or short leg walking cast with toe plate if pain is not adequately controlled with buddy taping |
| First metatarsal shaft | Axial load or crush injury; requires significantly more force than lesser metatarsals | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique foot radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography in one to two weeks to ensure stability, then four to six weeks after injury | Boot or short leg walking cast for three to four weeks, with weight-bearing as tolerated; use a short leg cast for patients with severe pain, and consider non–weight-bearing for initial one to two weeks; alternatively, hard-soled shoe for four to six weeks | Displaced, comminuted, intra-articular, or open fracture; concern for compartment syndrome | Increased risk of compartment syndrome in first metatarsal fractures (compared with other bones in the foot) First metatarsal is anatomically important for weight-bearing; alignment is crucial |
| Lesser (second through fourth) metatarsal shaft | Axial load or crush injury; twisting force when toes are fixed (e.g., caught in a narrow opening) and body/ambulation continues forward | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique foot radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography in one to two weeks to ensure stability, then four to six weeks after injury | Nondisplaced: short leg walking cast, boot, or hard-soled shoe for three to four weeks with weight-bearing as tolerated Fractures with more than 3 to 4 mm of displacement or more than 10 degrees of angulation should be reduced Postreduction: short leg non–weight-bearing cast or boot for three to four weeks followed by a short leg walking cast or boot for additional three to four weeks | Multiple metatarsal fractures, compartment syndrome, vascular compromise, open fracture, unable to reduce | Multiple metatarsal fractures should increase suspicion for Lisfranc joint disruption |
| Fifth metatarsal shaft | Rotational force while in plantar flexion | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique foot radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography in one to two weeks, then four to six weeks | Four weeks of immobilization with activity as tolerated (e.g., walking boot, hard-soled shoe) | > 3 to 5 mm of displacement after reduction, nonunion after six months, compartment syndrome, vascular compromise, open fracture | Pattern is usually oblique, progressing from distal-lateral to proximal-medial |
| Proximal fifth metatarsal | Zone 1: inversion injury Zones 2 and 3: landing on the side of the foot (adduction force while the foot is in plantar flexion) | Initial (zones 1 through 3): AP, lateral, and oblique foot radiography Follow-up: Zone 1: repeat radiography in six weeks if pain persists Zone 2: repeat at two- to four-week intervals Zone 3: repeat at four-week intervals | Zone 1: hard-soled shoe or short leg walking cast or boot with weight-bearing as tolerated; follow-up every two to four weeks and encourage mobility; casting, if used, should be limited to two weeks to ensure an early return to range of motion Zone 2: short leg non–weight-bearing cast for six weeks; then consider use of CAM boot for up to six weeks if patient is pain free with weight-bearing Zone 3: short leg non–weight-bearing cast for six to 20 weeks | Zone 1: > 2 to 3 mm displacement Zone 2: displaced, nonunion at three months, or patient refuses a cast; strongly consider referral regardless of status Zone 3: referral | Zone 1 fracture is the most common fracture of the lower extremities Zones 2 and 3 fractures have high rates of nonunion and slow healing |
| Midfoot | |||||
| Tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc) joint | Forceful abduction, twisting of a foot in plantar flexion; axial force (e.g., landing from a jump, stepping off a curb) | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique foot radiography Follow-up: consider CT for injury characterization and MRI for soft tissue evaluation; consider CT or MRI if radiographic findings are negative but there is high clinical suspicion for fracture | Short leg non–weight-bearing cast or boot for four to six weeks, followed by short leg weight-bearing cast or boot for two to four | Joint displacement > 2 mm, joint insta-bility (Table 4) | Estimated that 20% of Lisfranc fractures are initially overlooked; most Lisfranc injuries are unstable and will require surgery; reserve nonsurgical management for poor surgical candidates and patients without concerning radiographic findings (Table 4) |
| Midfoot | |||||
| Navicular | Avulsion fracture: plantar flexion with inversion or eversion Tuberosity fracture: eversion Body fracture: direct or axial load | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique foot weight-bearing radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography in four weeks, then every two weeks to monitor for nonunion | Body fracture: short leg walking cast or boot for six to eight weeks Dorsal or tuberosity avulsion fracture: short leg walking cast or boot for four to six weeks; can transition to a hard-soled shoe at four weeks if there is clinical evidence of healing Weight-bearing as tolerated for all; consider non–weight-bearing for concurrent extensive soft tissue injury | Dorsal avulsion fracture involving > 20% of the talonavicular joint Tuberosity avulsion fracture > 1 cm displacement Body fracture displacement > 1 mm, shortening > 2 mm, or evidence of nonunion at six to 10 weeks | 50% of navicular fractures are avulsion fractures |
| Cuboid and cuneiform | Direct trauma; indirect force resulting from a torsional motion of the midfoot | Initial: AP, lateral, and oblique foot weight-bearing radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography every two weeks | Short leg walking cast or boot for six weeks, with weight-bearing as tolerated, followed by six weeks of a hard-soled shoe or orthotics for arch support | Comminuted, significant displacement, or concurrent dislocation | Scar/callus formation as the bone heals can result in impaired function of peroneus longus tendon |
| Hindfoot | |||||
| Calcaneus | Direct trauma, axial loading of the bone, typically as a result of a fall from a height | Initial: AP, lateral, and Harris axial view foot/heel radiography Follow-up: repeat radiography every two to four weeks | Short leg non–weight-bearing cast or boot for four to six weeks | Comminuted, displacement > 2 mm, > 25% involvement of calcaneal cuboid joint, nonunion after six weeks | Harris axial view is performed with the foot in dorsiflexion and angled 45 degrees cephalad 10% of calcaneal fractures have associated acute compartment syndrome Can tolerate more displacement in patients with multiple medical comorbidities; treat non-surgically if there is a concern for poor healing |
Anatomy
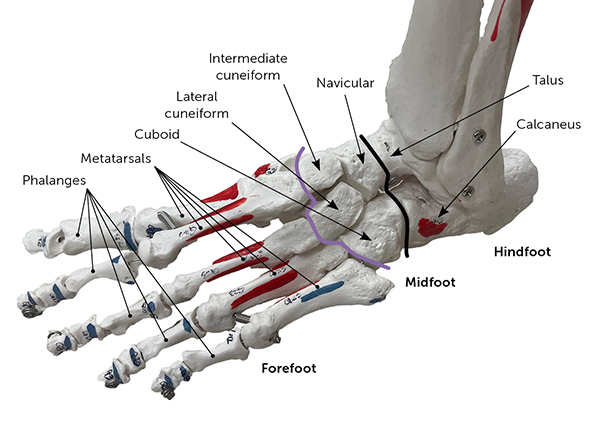
The foot is made up of 26 bones. It is divided into the hind-foot (talus and calcaneus), midfoot (cuboid, navicular, and cuneiform), and forefoot (metatarsals and phalanges). The forefoot is connected to the midfoot through the tarsometatarsal, or Lisfranc, joint. This is a gliding joint between the medial cuneiform and base of the second metatarsus that is critical for foot stability and dispersion of force during ambulation. Figure 1 shows the bony anatomy of the foot. [corrected]
Physical Examination
A systematic examination of the foot includes inspection of the skin and nails for swelling, deformity, open wounds, or ecchymosis.14 Inability to fully bear weight with ambulation may suggest a fracture. Palpation of the foot should be performed systematically, with special focus on examination of the painful area and focal tenderness over bony prominences.15 Range of motion assessment should include active and passive movements of the ankle and toes. Neurovascular assessment should be performed with palpation of the dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses, evaluation of capillary refill, and sensory testing.
Imaging
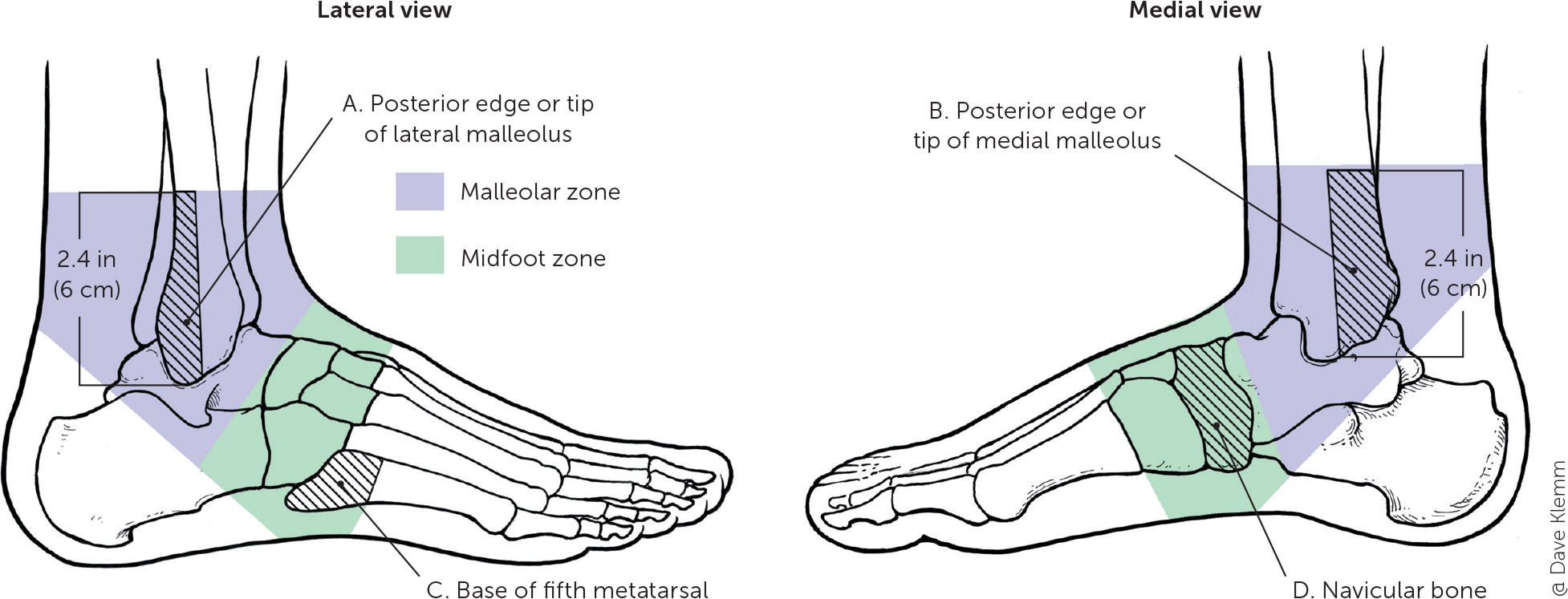
When a foot or toe fracture is suspected, weight-bearing anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique radiography of the foot and dedicated toe radiography should be obtained.4,5,16 The Ottawa foot and ankle rules (Table 215 and Figure 215) can be used to determine the need for radiography for an acute ankle inversion injury.4,5,15 Avulsion fractures in the midfoot can have specific radiographic findings (Table 3).17 Computed tomography should be considered if radiography does not show a fracture but clinical suspicion is high. Magnetic resonance imaging can be helpful when there is suspected soft tissue (i.e., ligament or tendon) injury.11,12,16 If computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is not available and there is high clinical suspicion for fracture, a fracture can be assumed until radiography is repeated in seven to 10 days.4
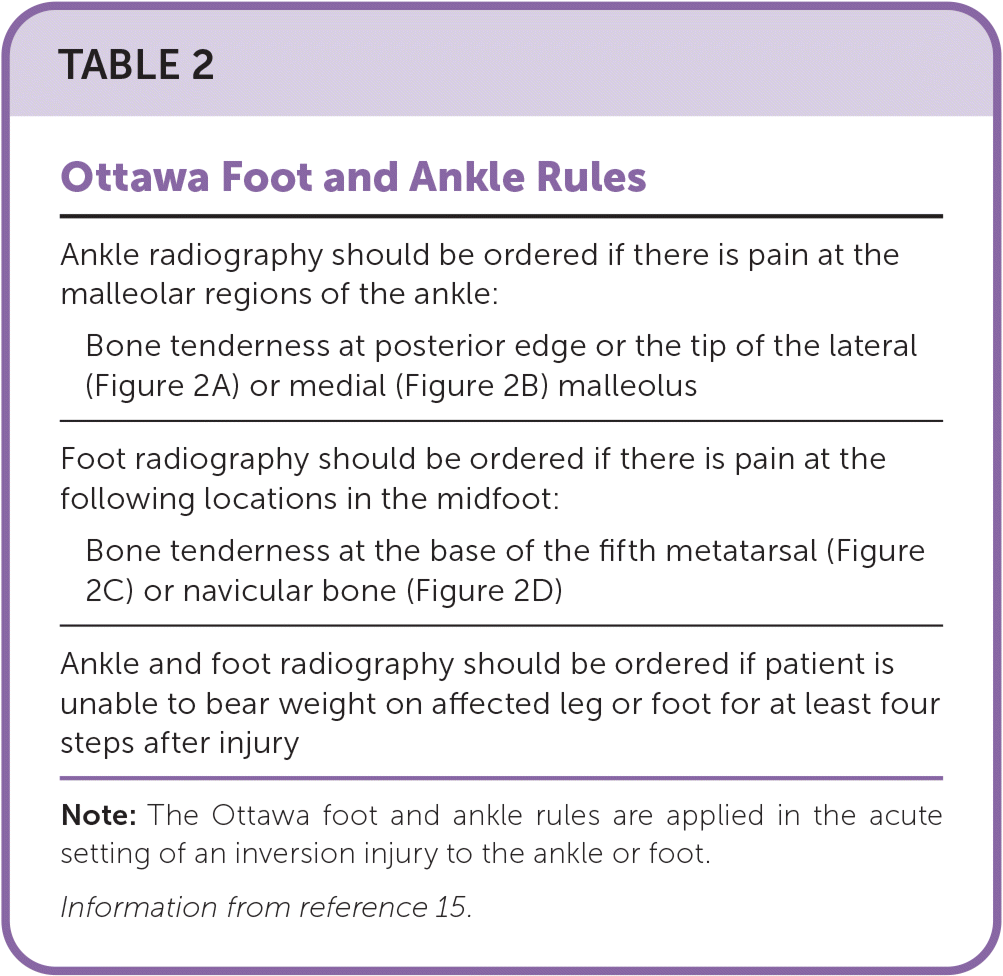
| Ankle radiography should be ordered if there is pain at the malleolar regions of the ankle: |
| Bone tenderness at posterior edge or the tip of the lateral (Figure 2A) or medial (Figure 2B) malleolus |
| Foot radiography should be ordered if there is pain at the following locations in the midfoot: |
| Bone tenderness at the base of the fifth metatarsal (Figure 2C) or navicular bone (Figure 2D) |
| Ankle and foot radiography should be ordered if patient is unable to bear weight on affected leg or foot for at least four steps after injury |
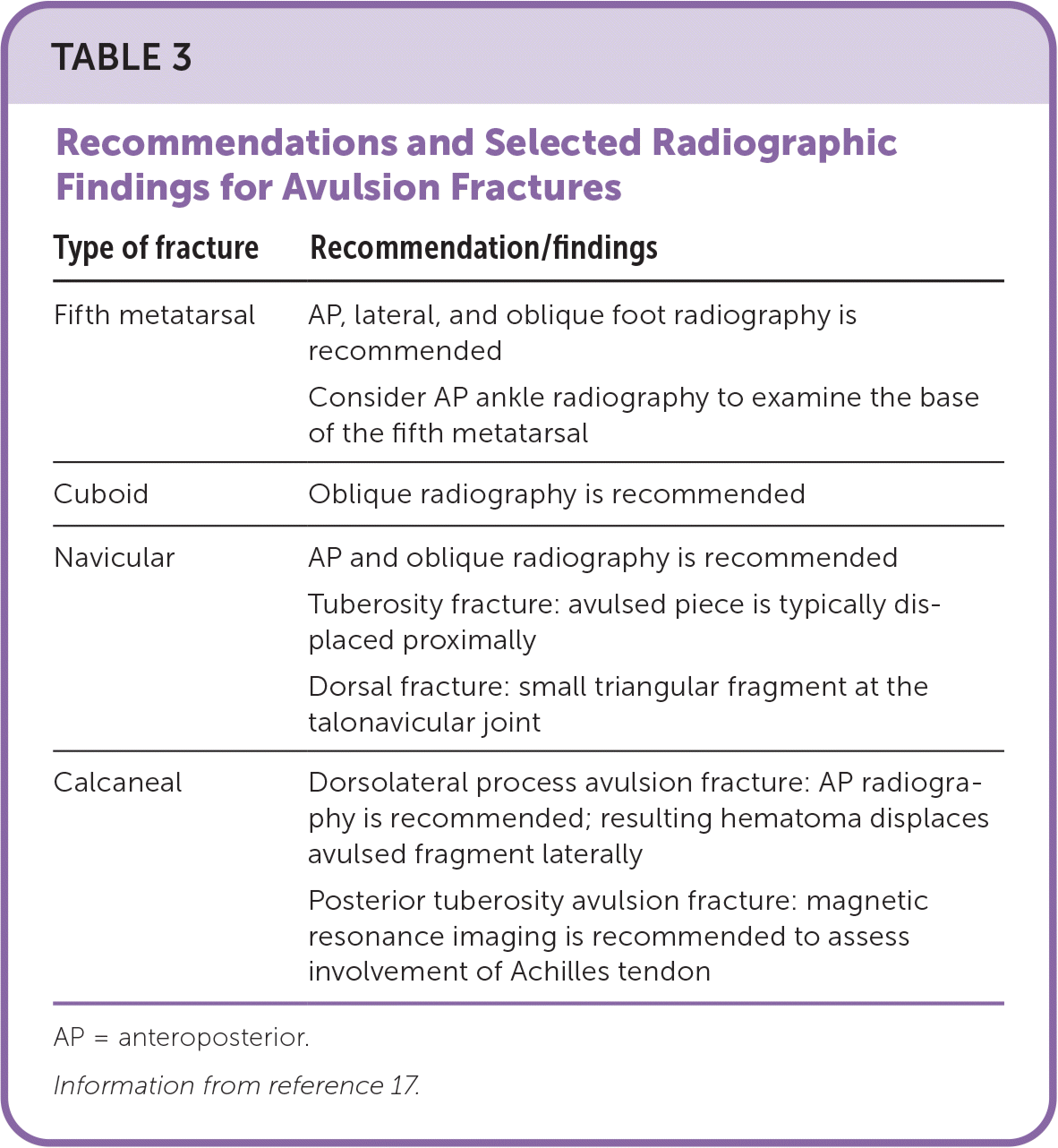
| Type of fracture | Recommendation/findings |
|---|---|
| Fifth metatarsal | AP, lateral, and oblique foot radiography is recommended |
| Consider AP ankle radiography to examine the base of the fifth metatarsal | |
| Cuboid | Oblique radiography is recommended |
| Navicular | AP and oblique radiography is recommended |
| Tuberosity fracture: avulsed piece is typically displaced proximally | |
| Dorsal fracture: small triangular fragment at the talonavicular joint | |
| Calcaneal | Dorsolateral process avulsion fracture: AP radiography is recommended; resulting hematoma displaces avulsed fragment laterally |
| Posterior tuberosity avulsion fracture: magnetic resonance imaging is recommended to assess involvement of Achilles tendon |
Forefoot: Phalangeal Fractures
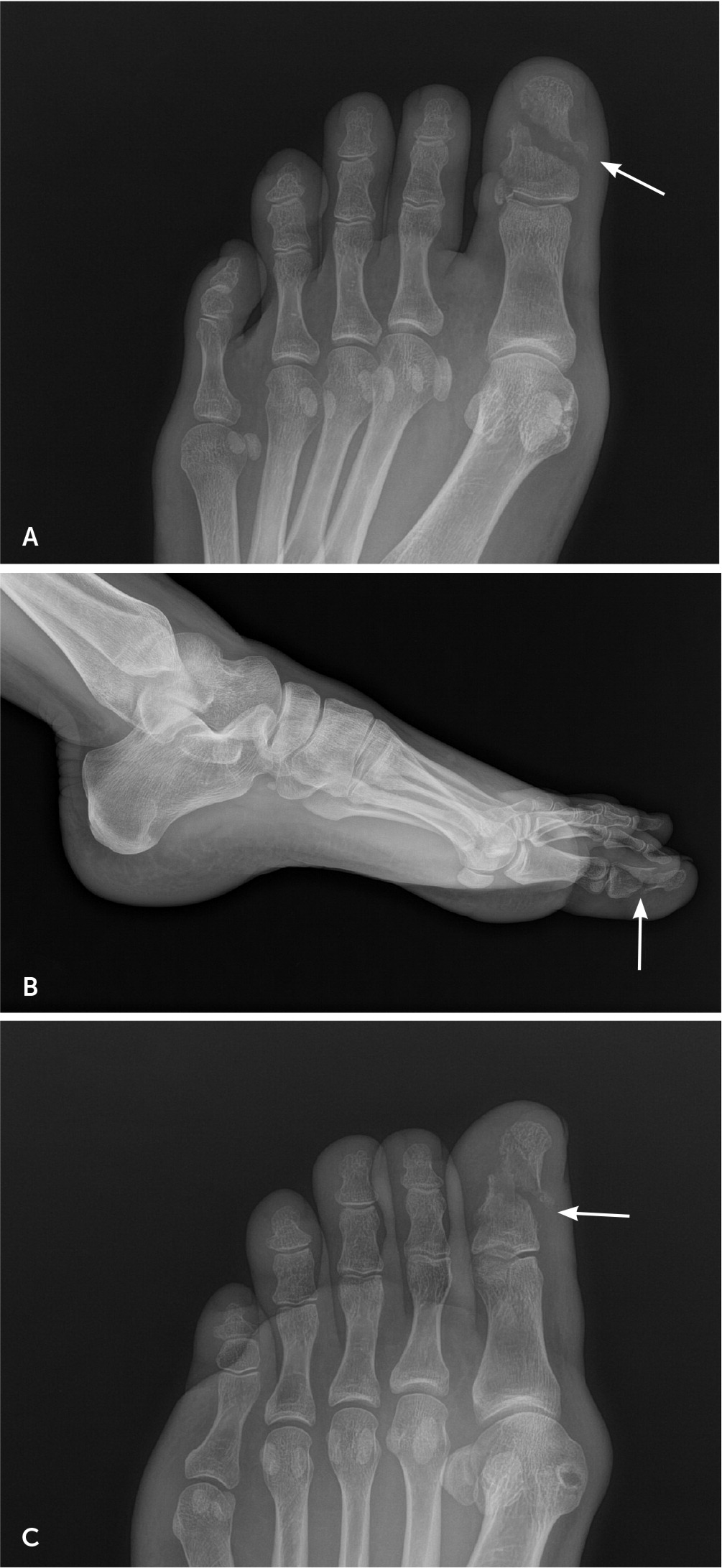
Toe fractures make up 3% to 8% of lower extremity fractures.1,18 They typically result from axial loading by “stubbing” the toe or a crush injury. The great toe is the most commonly fractured toe and is associated with higher morbidity due to its role in weight-bearing, balance, and toe-off during ambulation. This type of fracture is also more likely to require surgical intervention.6,18,19
If the fracture is displaced, deformity of the toe may be present. Rotational fracture deformity is suggested when the nail bed of the affected toe lies in a different plane than adjacent toes or the same toe on the opposite foot.15
GREAT TOE
Initially, most great toe fractures (Figure 3) can be managed with a walking boot or short leg walking cast for two to three weeks, followed by an additional two to three weeks of buddy taping and a hard-soled shoe. The decision to transition to a less restrictive option should be based on the absence of pain at the fracture site. Radiography should be repeated one to two weeks after the injury to assess healing and fracture stability if the pain persists.
LESSER TOES
Stable, nondisplaced toe fractures are treated nonsurgically with immobilization by buddy taping the fractured toe to the adjacent toe. A hard-soled shoe (i.e., tennis shoe or boot) or postoperative shoe should be used until point tenderness has resolved, approximately three to six weeks after the injury. Pain should be reassessed one to two weeks after the initial injury. Repeat radiography is needed only if there is no improvement.4 Physicians should consider the use of a walking boot or short leg walking cast with a toe plate if pain is not adequately controlled.
INDICATIONS FOR REFERRAL
Indications for referral include neurovascular compromise, contaminated wounds, or open fractures. Lesser toe fractures rarely require surgical intervention, but patients with fracture of any toe should be referred if there is evidence of rotation, a displaced intra-articular fracture, severe crush injury, or a fracture that involves more than 25% of the inter-phalangeal joint space.4,5,15
Forefoot: Metatarsal Fractures
Metatarsal fractures occur from an axial load, twisting force, or crush injury. Applying an axial load to the metatarsal in the direction of the calcaneus (i.e., pushing the corresponding toe toward the affected metatarsal) will usually elicit pain at the fracture site.20
FIRST METATARSAL SHAFT
The first metatarsal is critical for weight-bearing and ambulation due to its articulation with the great toe. Non-displaced first metatarsal fractures can be managed using a short leg walking cast, boot, or hard-soled shoe for three to six weeks, with weight-bearing as tolerated.4,5 Follow-up with radiography should be performed in one to two weeks to ensure maintained alignment and then four to six weeks after injury. Patients with displaced, comminuted, intra-articular, or open first metatarsal fractures should be referred.4,5
LESSER (SECOND THROUGH FOURTH) METATARSAL SHAFT
Displacement is rare in this group unless there are multiple metatarsal fractures. Nonsurgical management includes immobilization with a short leg walking cast, boot, or hard-soled shoe for three to four weeks, with weight-bearing as tolerated.
FIFTH METATARSAL SHAFT
Fifth metatarsal shaft fractures are usually oblique and spiral (Figure 4). Recent literature has supported nonsurgical management regardless of displacement if there is no rotational deformity. Two retrospective case series of 33 and 37 patients reported healing with good functional outcomes for all fractures in an average of 8.3 to 12.3 weeks. Immobilization was achieved with use of a walking boot, hard-soled shoes, or normal footwear, based on patient comfort, with activity as tolerated.22,23 These studies support an approach of starting with four weeks of immobilization and weight-bearing as tolerated. Subjective pain scores can guide subsequent management.24 Indications for referral include the need for reduction and nonunion at six months.22,23
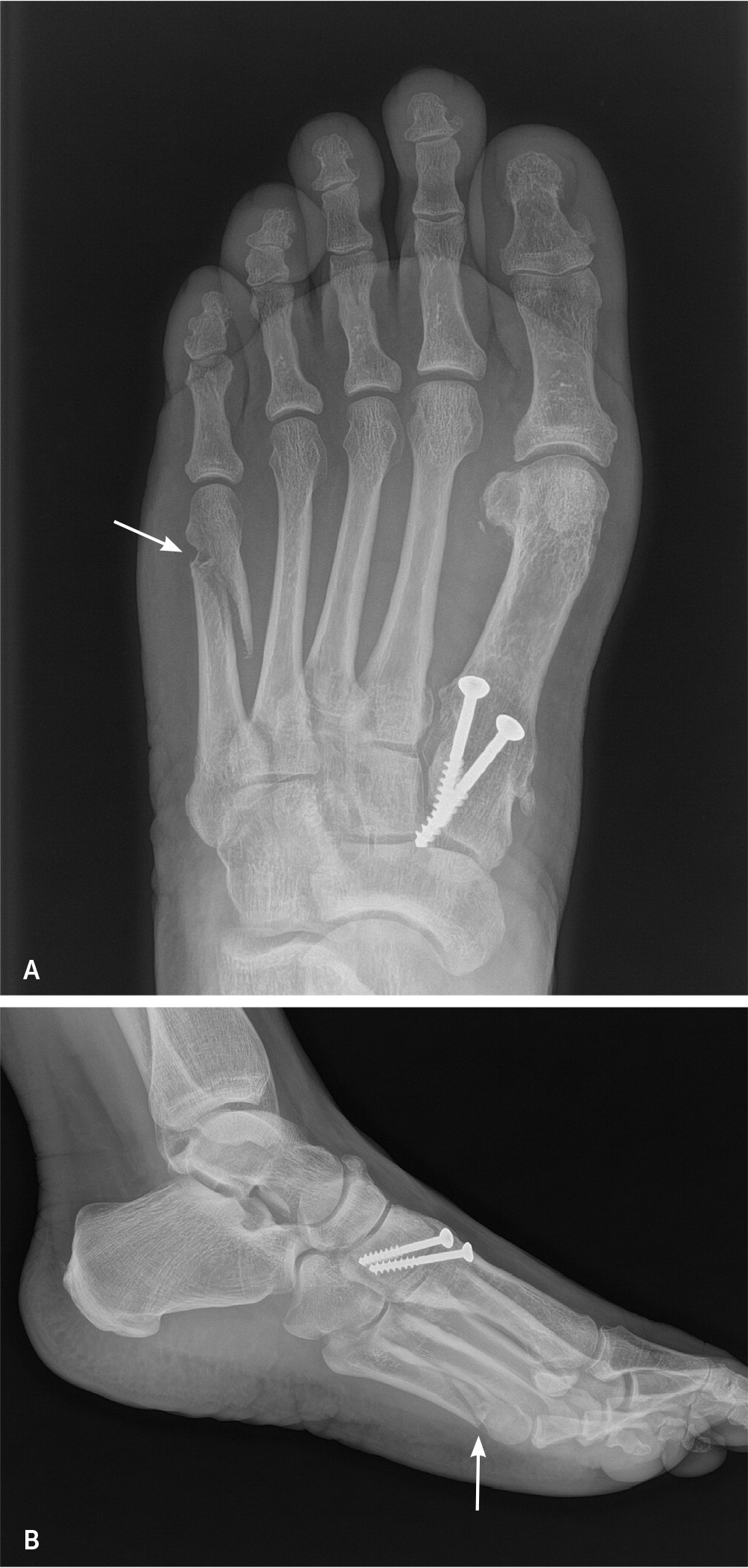
PROXIMAL FIFTH METATARSAL
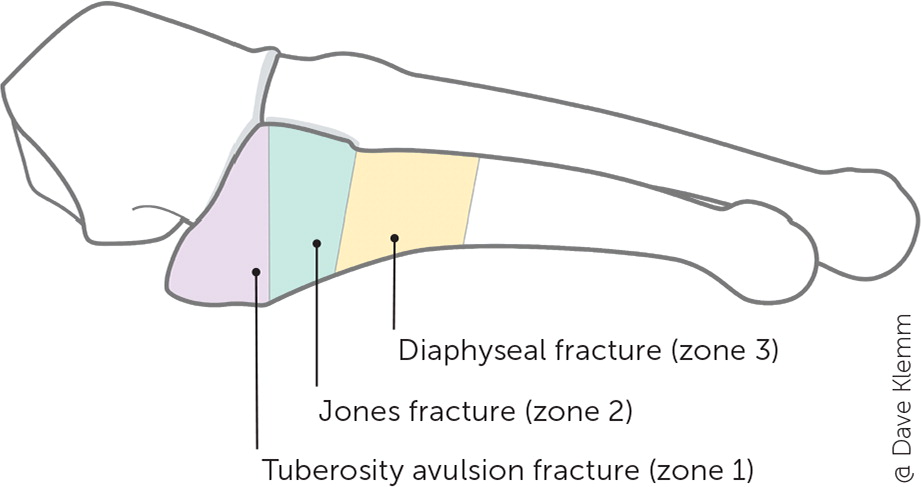
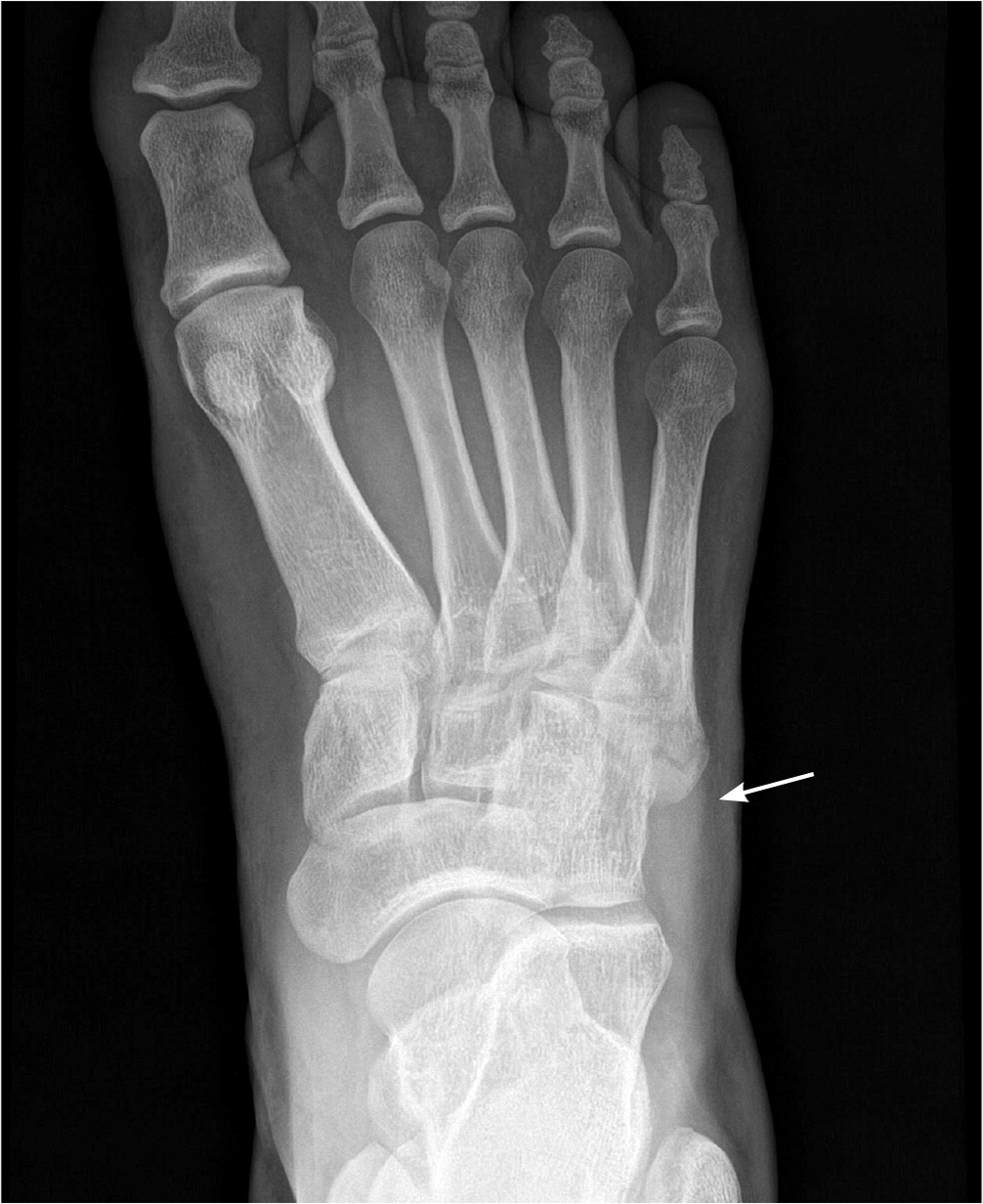
Zone 1 fractures are referred to as tuberosity avulsion fractures4,5 (Figure 6). Management includes a hard-soled shoe or short leg walking cast or boot, with weight-bearing as tolerated; casting should be limited to two weeks to ensure an early return to range of motion. Total treatment duration is symptom driven, and patients usually heal within four to eight weeks. If pain lasts longer than six weeks, radiography should be repeated to ensure adequate healing.8,9
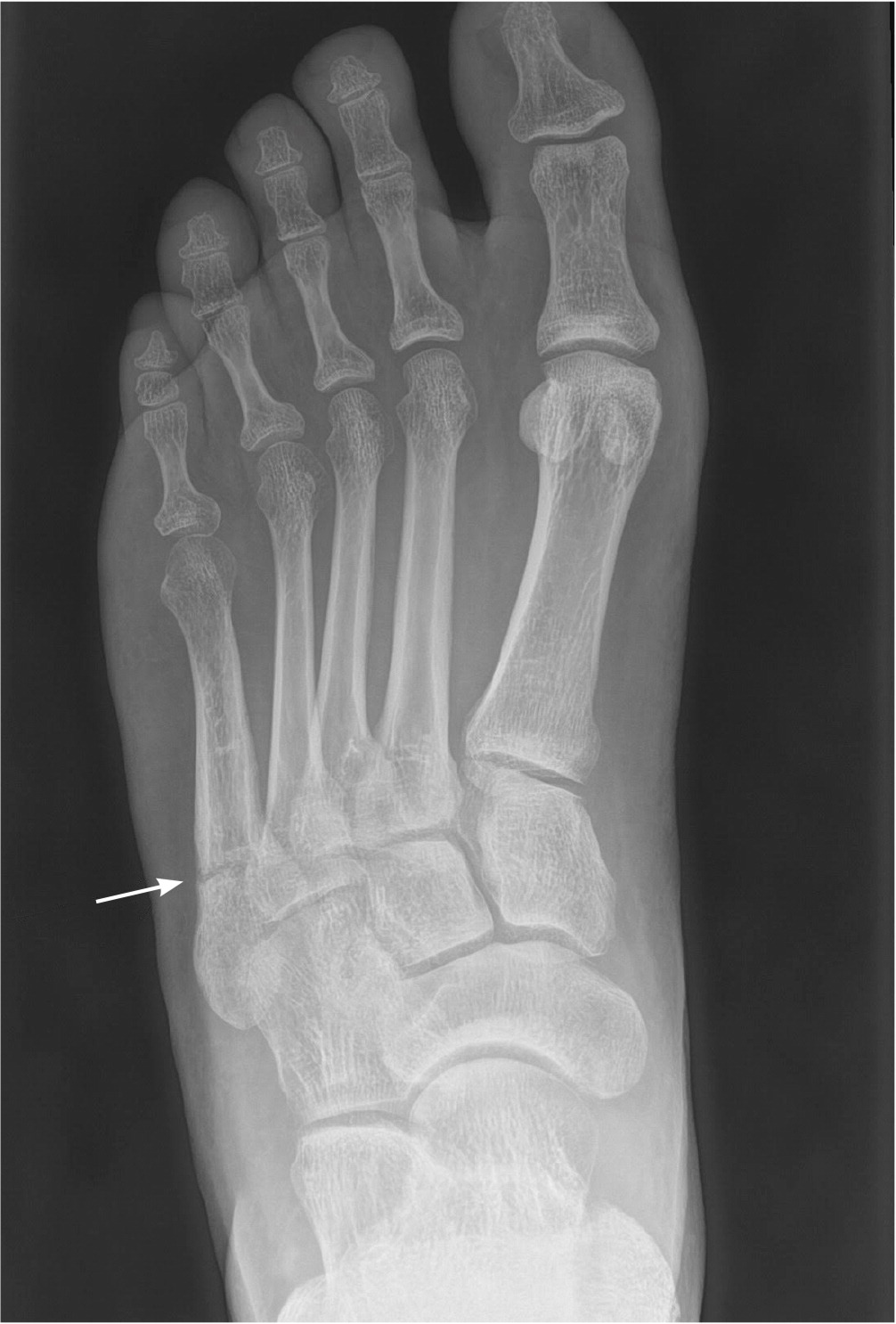
Zone 2 (Jones) fractures occur at the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction (Figure 7). This junction is located at the fourth and fifth metatarsal joint. The mechanism of injury is traumatic forced adduction applied laterally while the foot is in plantar flexion. These fractures are complicated by the risk of nonunion and slow healing due to poor blood supply; therefore, surgical management should be considered. Conservative management includes a short leg non–weight-bearing cast for six weeks followed by protected weight-bearing with a short leg non–weight-bearing cast or controlled ankle motion (CAM) boot for another one to six weeks based on radiographic and clinical healing.4,5
Zone 3 fractures occur at the proximal 1.5 cm of the diaphysis, most commonly as a result of microtrauma to the region. Surgical management is similar to a zone 2 fracture.9,25 However, due to the nature of a zone 3 injury, nonsurgical management is longer, with strict use of a short leg non–weight-bearing cast for up to 20 weeks.4,5
Patients with an avulsion fracture that has greater than 2 to 3 mm of displacement should be referred. Referral should be strongly considered in active patients with fractures in zone 2 or 3 to decrease the risk of nonunion.8,9 In a systematic review that included 237 patients with zone 2 fractures, the nonunion rate was 11% to 50% in the 121 patients who were managed nonsurgically, compared with 0% to 11% in the 116 patients who were managed surgically.25 Patients with zone 2 fractures that are managed nonsurgically should be referred if there is nonunion after three months.
Midfoot Fractures (Tarsometatarsal, Navicular, Cuboid, Cuneiform)
Midfoot fractures are the least common foot fractures due to the many ligaments stabilizing the tarsal bones. The mechanism of injury is an axial load causing inversion of a plantar flexed foot (e.g., landing from a jump, stepping off a curb) or direct trauma. These types of fractures are subtle and may be missed on imaging, resulting in chronic pain, instability, and arch collapse. Tenderness to palpation of the dorsomedial foot should increase suspicion for a navicular fracture. Midfoot swelling, especially at the medial border of the first tarsometatarsal joint, and plantar ecchymosis suggest a possible tarsometatarsal (i.e., Lisfranc) injury.12,26,27
Injuries to the tarsometatarsal complex include ligamentous disruption at the joint, with or without fracture of the adjacent tarsal bone (Figure 8). Fractures of the tarsal bones suggest a more extensive injury and must be carefully evaluated (Table 4).11,12,27 Stable tarsometatarsal fractures can be managed with a short leg non–weight-bearing cast or boot for four to six weeks, followed by two to four weeks in a short leg weight-bearing cast or boot.12
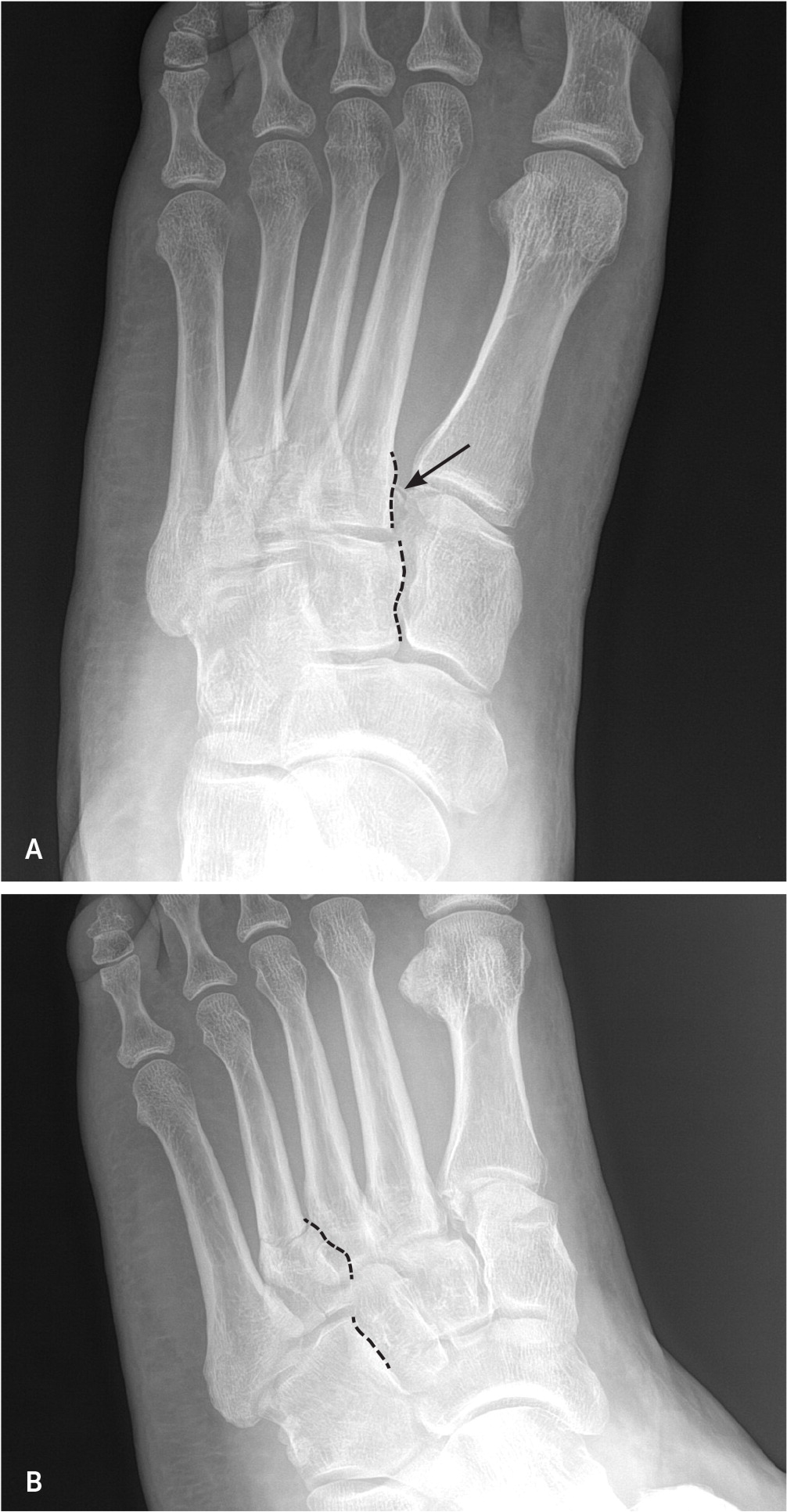
Avulsion and nondisplaced navicular body fractures can be managed with a short leg walking cast or boot for six to eight weeks, with weight-bearing as tolerated. If the patient has significant swelling or pain with ambulation, an initial four to six weeks of non–weight-bearing should be considered because serious ligamentous injury may have occurred.10 Patients with dorsal avulsion and tuberosity fractures can be transitioned to a hard-soled shoe at four weeks if there is evidence of healing.10,28 Cuboid and cuneiform fractures are managed with six weeks of a short leg walking cast or boot, followed by six weeks of additional arch support.4,5,10,28
Hindfoot (Calcaneus)
Calcaneal fractures that are nondisplaced and do not involve more than 25% of the calcaneal cuboid joint can be managed nonsurgically, with four to six weeks in a short leg non–weight-bearing cast or boot.13 Hind-foot fractures that are comminuted, are displaced, or demonstrate nonunion after six weeks require referral.4–13
Foot Fracture Complications
Complications include arthritis, infection, mal-union or nonunion, and compartment syndrome. There is an increased risk of long-term arthritis with intra-articular fractures and acute infection in open fractures. If there is concern for malunion due to extensive displacement or angulation, imaging should be repeated at one week. Although nonunion can occur in any bone in the foot, it is most likely in zone 2 of the fifth metatarsal. Because of the significant traumatic force that causes calcaneal fractures, compartment syndrome can occur in up to 10% of cases.2 First metatarsal fractures are also at risk of compartment syndrome due to their proximity to the dorsalis pedis artery, which can lead to increased bleeding and swelling.4 A neurovascular examination before casting and then one day after casting can detect early neurovascular compromise. Patient education on reporting an uncomfortable cast, numbness and tingling, or skin changes is imperative.4
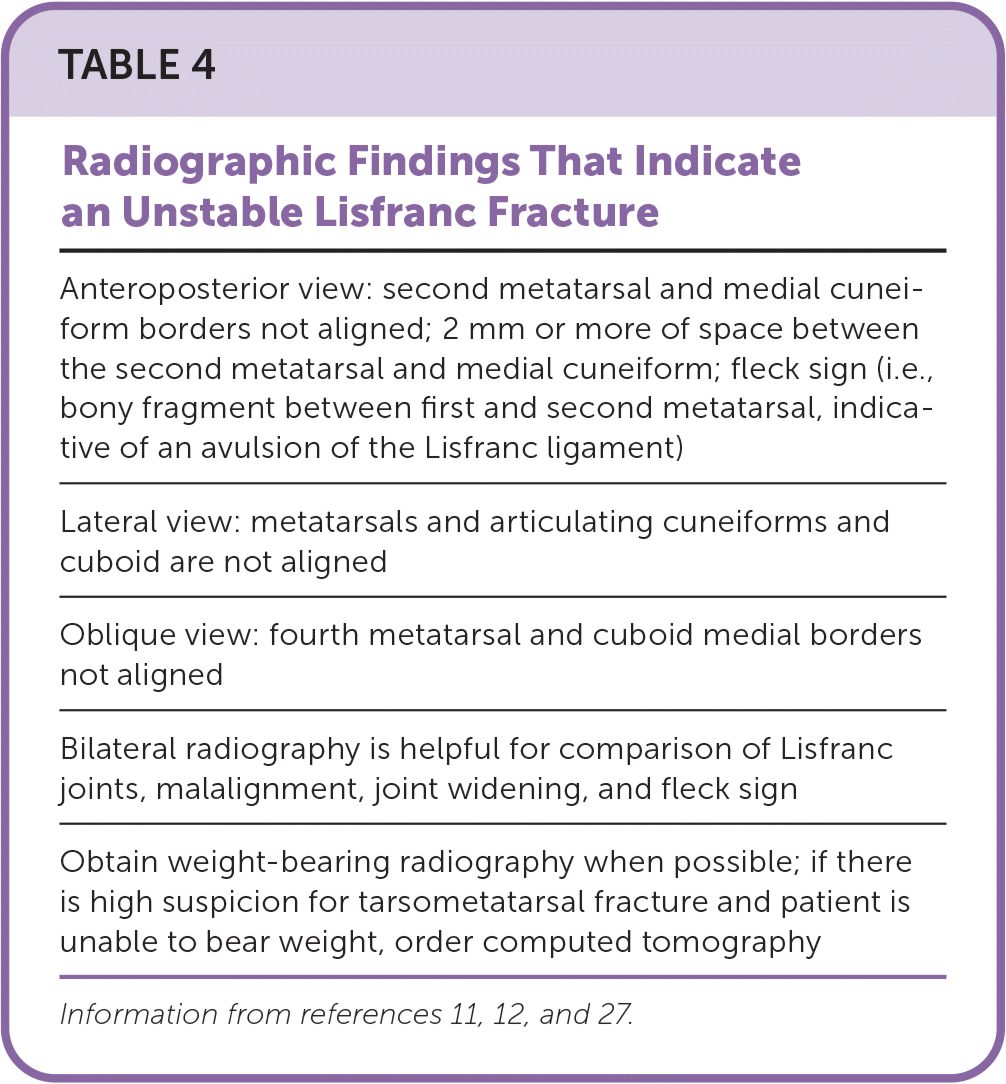
| Anteroposterior view: second metatarsal and medial cuneiform borders not aligned; 2 mm or more of space between the second metatarsal and medial cuneiform; fleck sign (i.e., bony fragment between first and second metatarsal, indicative of an avulsion of the Lisfranc ligament) |
| Lateral view: metatarsals and articulating cuneiforms and cuboid are not aligned |
| Oblique view: fourth metatarsal and cuboid medial borders not aligned |
| Bilateral radiography is helpful for comparison of Lisfranc joints, malalignment, joint widening, and fleck sign |
| Obtain weight-bearing radiography when possible; if there is high suspicion for tarsometatarsal fracture and patient is unable to bear weight, order computed tomography |
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Bica, et al.15
Data Sources: A search was performed in PubMed, Google Scholar, Cochrane database, and Essential Evidence Plus. Key words included epidemiology foot fractures, foot fractures, metatarsal fractures, midfoot fractures, toe fractures, ultrasound of fractures, Lisfranc injury, and proximal fifth metatarsal injury. Search dates: September and December 2022, and May, July, and November 2023.
The opinions and assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, U.S. Department of Defense, U.S. Air Force, or U.S. government.